blog»Digital Marketing»Step-by-Step Guide to Formulating a Hypothesis for A/B Testing

Step-by-Step Guide to Formulating a Hypothesis for A/B Testing
2024/07/16
You can read this article in about 27 minutes
Introduction
A/B testing is a powerful tool for e-commerce marketers. It helps you make data-driven decisions to improve your website’s performance. But to get the most out of A/B testing, you need a solid hypothesis. Without a clear hypothesis, your tests can become directionless, wasting time and resources.
Creating a hypothesis might seem daunting, but it doesn’t have to be. Think of it as your testing blueprint. A well-crafted hypothesis guides your test, ensuring you focus on the right changes and measure the correct outcomes.
In this article, we’ll break down the process into simple steps. You’ll learn how to identify the problem you want to solve, gather the necessary data, and define your variables. We’ll also cover how to formulate, review, and refine your hypothesis to make it actionable and effective.
By following these steps, you’ll be able to create hypotheses that lead to meaningful insights and improvements. Whether you’re looking to boost conversion rates, reduce bounce rates, or enhance user engagement, a strong hypothesis is your first step to success. Let’s dive in and start crafting better A/B testing hypotheses together.
Step 1: Identify the Problem or Research Question
The first step in creating a strong A/B testing hypothesis is to clearly identify the problem you want to solve. This sets the stage for your entire test and ensures you’re focused on making meaningful improvements.

Start by looking at your website’s performance metrics. Are there areas where you’re underperforming? Common problems in e-commerce include low conversion rates, high bounce rates, or poor user engagement. Pinpoint the specific issue that, if improved, would have the most significant impact on your business.
Next, ask yourself why this problem might be occurring. Is your call-to-action (CTA) button hard to find? Is your product description too lengthy or unclear? Understanding the root cause helps you frame your hypothesis around a potential solution.
For example, let’s say you notice a high bounce rate on your product pages. Your research question might be: “Why are users leaving our product pages without adding items to their cart?” This question leads you to consider potential reasons and solutions.
By clearly defining the problem or research question, you lay a solid foundation for your A/B test. This clarity ensures that your hypothesis will be focused and relevant, leading to more actionable insights.
Step 2: Gather Data and Insights
Once you’ve identified the problem, it’s time to gather data and insights. This step is crucial because data-driven decisions are far more effective than guesses or assumptions.
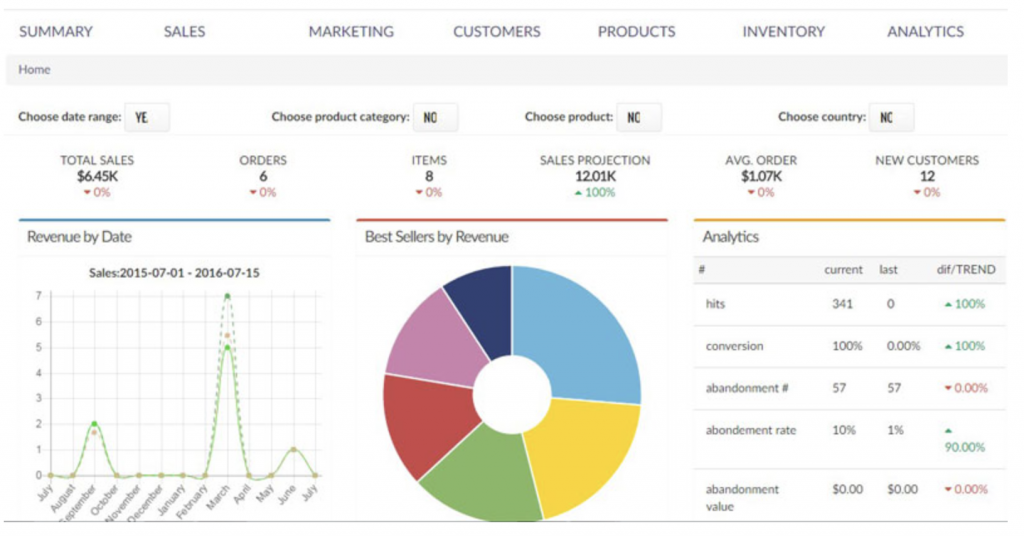
Start by diving into your analytics. Tools like Google Analytics or Ptengine can provide a wealth of information about user behavior on your site. Look for patterns and anomalies. For instance, you might find that a significant percentage of users drop off at a specific point in the checkout process.
In addition to quantitative data, consider gathering qualitative insights. User feedback, surveys, and usability tests can offer valuable perspectives that numbers alone can’t provide. For example, a survey might reveal that users find your checkout process confusing or that product descriptions lack crucial details.
Here are a few ways to gather data:
- Analytics Tools: Use these to track metrics like page views, bounce rates, and conversion rates.
- Heatmaps: Tools like Ptengine can show where users click, scroll, and spend the most time.
- Surveys and Feedback Forms: Direct input from users about their experiences and pain points.
- User Testing: Observing real users as they navigate your site to identify usability issues.
By combining these data sources, you get a clearer picture of the problem. This comprehensive understanding is key to forming a hypothesis that addresses the root cause rather than just treating the symptoms.
Armed with this data, you can confidently move on to defining your variables, knowing that your hypothesis will be grounded in solid evidence.
Step 3: Define Your Variables
Now that you’ve gathered data and insights, it’s time to define your variables. In A/B testing, variables are the elements you change and measure to see if they impact your desired outcome.
Independent Variable: This is what you will change in your test. It should be a single element, like a headline, image, or button color. Keeping it simple ensures that you can accurately attribute any changes in your results to this specific element.
Dependent Variable: This is what you will measure to determine the effect of your change. Common dependent variables in e-commerce include conversion rates, click-through rates, bounce rates, and average order value. Choose a metric that aligns with your goals and provides a clear indication of performance.
For example, if your problem is a low conversion rate on product pages, your independent variable could be the product description length. You might hypothesize that shorter, more concise descriptions will lead to higher conversions. Your dependent variable would then be the conversion rate on those product pages.
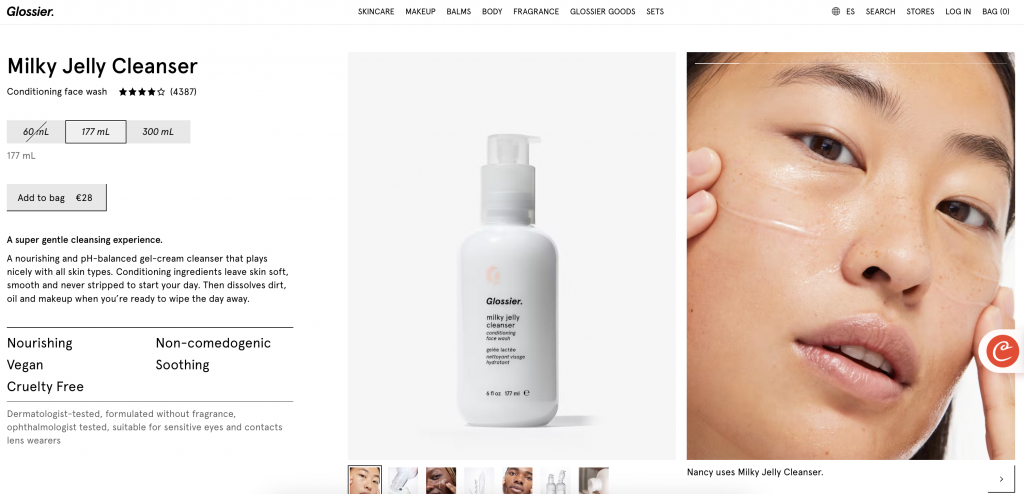
Here’s a simple way to define your variables:
- Identify the Change: What specific element will you modify? (e.g., CTA button color)
- Set the Metric: How will you measure success? (e.g., click-through rate)
Example:
- Independent Variable: The color of the CTA button on the product page.
- Dependent Variable: The click-through rate of the CTA button.
By clearly defining these variables, you set the stage for a precise and focused test. This clarity helps ensure that your results will be reliable and actionable, giving you the insights needed to make informed decisions.
Step 4: Formulate Your Hypothesis
With your variables defined, it’s time to formulate your hypothesis. A strong hypothesis clearly states the expected outcome of your test and provides a rationale for why you expect this result. It serves as a blueprint for your A/B test, guiding your actions and helping you stay focused on the goal.
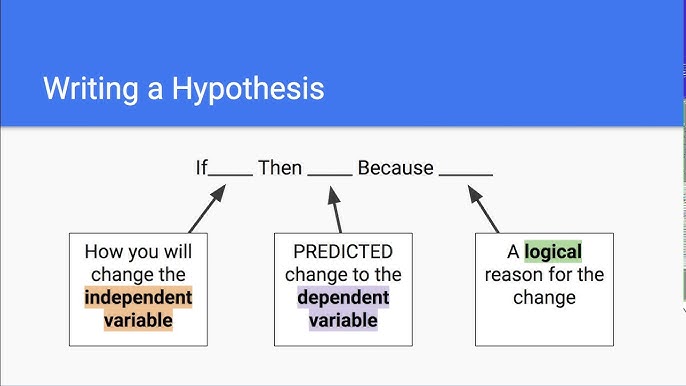
A good hypothesis follows a simple structure: “If [independent variable], then [expected outcome] because [rationale].”
Here’s how to build it:
- Start with the Change (Independent Variable): Specify the element you plan to change.
- State the Expected Outcome (Dependent Variable): Describe what you expect to happen as a result of this change.
- Provide a Rationale: Explain why you think this change will lead to the expected outcome, based on the data and insights you’ve gathered.
Example:
- If we change the color of the CTA button from blue to green, then the click-through rate will increase because green is more visually prominent and associated with positive action.
Another example:
- If we shorten the product description, then the conversion rate will increase because users can quickly grasp the key benefits without feeling overwhelmed by too much text.
When writing your hypothesis, keep it specific and testable. Avoid vague statements like “improve user experience” without specifying how you will measure this improvement. Your hypothesis should be clear enough that anyone reading it understands what you are testing and why.
A well-formulated hypothesis sets a clear direction for your A/B test. It helps you focus on making meaningful changes and provides a basis for measuring success. This clarity ensures that your test will yield actionable insights, helping you make data-driven decisions that enhance your e-commerce performance.
Step 5: Ensure Your Hypothesis is Specific and Actionable
To get the most out of your A/B testing, your hypothesis needs to be both specific and actionable. This means it should be clear, focused, and feasible to test within a reasonable timeframe. Specificity helps you stay on track and measure the right outcomes, while actionability ensures you can implement the necessary changes and run the test effectively.
Make It Specific:
- Clear Definitions: Avoid vague terms. Define exactly what you are changing and how you will measure the outcome.
- Single Focus: Stick to one change per hypothesis to isolate the impact of that change.
- Targeted Segment: If applicable, specify which segment of your audience you are targeting. This helps in understanding the context of the results.
Example of a specific hypothesis:
- If we change the “Add to Cart” button text from “Buy Now” to “Add to Bag” on mobile product pages, then the conversion rate for mobile users will increase because the new text aligns better with user expectations and common shopping behavior.
Ensure Actionability:
- Feasible Implementation: Ensure the change you want to test can be easily implemented without requiring extensive development time or resources.
- Measurable Outcome: Choose an outcome that can be easily tracked and measured with your existing analytics tools.
- Reasonable Timeframe: Make sure the test can run long enough to gather sufficient data but not so long that it delays decision-making.
Example of an actionable hypothesis:
- If we add a trust badge next to the checkout button, then the checkout completion rate will increase because users will feel more secure making a purchase.
Tips for Specific and Actionable Hypotheses:
- Narrow Focus: Instead of trying to test multiple changes at once, break them down into separate hypotheses.
- Simple Metrics: Use straightforward metrics that directly relate to your business goals.
- Quick Wins: Start with changes that are easy to implement and test, providing quick insights that can inform larger projects.
By ensuring your hypothesis is specific and actionable, you set yourself up for a successful A/B test. This approach helps you focus on changes that can be effectively tested and measured, leading to clear, actionable insights that drive real improvements in your e-commerce performance.
Step 6: Test for Feasibility and Prioritize
Before you dive into running your A/B test, it’s crucial to assess the feasibility of your hypothesis and prioritize it among other potential tests. This ensures you’re investing your time and resources in the most impactful and practical tests.
Evaluate Feasibility:
- Technical Requirements: Determine if the changes required for your test are technically feasible. Do you have the necessary tools and resources to implement the changes?
- Resource Allocation: Consider the time, effort, and cost involved. Can your team handle the workload without impacting other projects?
- Sample Size: Ensure you have a large enough audience to run the test and get statistically significant results. Use tools like sample size calculators to estimate how many users you’ll need.
Example of evaluating feasibility:
- If your hypothesis involves a major redesign of your checkout process, you’ll need to ensure your development team has the capacity to make these changes and that you can test with enough users to draw valid conclusions.
Prioritize Your Hypotheses:
- Expected Impact: Prioritize hypotheses based on the potential impact on your key metrics. Will the change likely result in a significant improvement?
- Ease of Implementation: Start with tests that are easier and quicker to implement. Quick wins can provide valuable insights and momentum.
- Business Goals: Align your tests with your current business goals. If your main goal is to increase conversions, prioritize hypotheses aimed at improving conversion rates.
Example of prioritizing hypotheses:
- If you have several hypotheses, rank them based on factors like potential ROI, alignment with business objectives, and the simplicity of implementation. A hypothesis that promises a high impact on conversion rates and is easy to implement should take precedence over one that is complex and offers marginal gains.
Creating a Prioritization Framework:
- Scoring System: Develop a scoring system to rank your hypotheses. For example, score each hypothesis on impact, ease, and alignment with goals, then add up the scores to determine priority.
- Regular Review: Revisit and adjust your priorities regularly based on new data and insights. Business priorities can shift, and so should your testing focus.
By evaluating feasibility and prioritizing your hypotheses, you ensure that your A/B tests are practical and aligned with your business objectives. This approach helps you focus on the most promising and manageable tests, maximizing your chances of achieving meaningful results and driving continuous improvement in your e-commerce performance.
Step 7: Review and Refine Your Hypothesis
After defining, evaluating, and prioritizing your hypothesis, it’s time to review and refine it. This step ensures that your hypothesis is as strong and effective as possible before you start your A/B test.

Peer Review:
- Get Feedback: Share your hypothesis with colleagues or stakeholders for feedback. Fresh eyes can catch potential issues or suggest improvements.
- Cross-Disciplinary Input: Seek input from different departments such as marketing, UX/UI, and development. Each perspective can provide valuable insights.
Example of peer review:
- Present your hypothesis to the marketing team to ensure it aligns with overall strategy, and to the development team to confirm technical feasibility.
Refinement Tips:
- Clarity and Precision: Make sure your hypothesis is crystal clear. Remove any ambiguous language. Anyone reading it should understand exactly what you’re testing and why.
- Focus on Specifics: Revisit your variables and outcomes to ensure they are specific and measurable. Fine-tune the details to eliminate any vagueness.
- Iterate Based on Feedback: Use the feedback from your peers to make necessary adjustments. Sometimes, small tweaks can significantly strengthen your hypothesis.
Example of refining a hypothesis:
- Original: “If we improve the product page design, then conversion rates will increase.”
- Refined: “If we add a customer review section to the product page, then conversion rates will increase because reviews provide social proof and build trust.”
Testing and Adjustments:
- Pilot Tests: Before a full-scale rollout, consider running a small-scale pilot test. This helps validate your hypothesis and identify any unforeseen issues.
- Continuous Improvement: Even after refining, be prepared to iterate based on the test results. Testing is an ongoing process of learning and optimizing.
Final Checklist:
- Specific and Clear: Is your hypothesis clearly stated and specific?
- Actionable: Can you easily implement and measure the changes?
- Feasible: Do you have the resources and sample size needed?
- Prioritized: Does it align with your business goals and priorities?
By thoroughly reviewing and refining your hypothesis, you ensure that your A/B test is set up for success. A well-crafted hypothesis leads to more reliable results, providing the insights needed to make informed decisions and drive improvements in your e-commerce strategy.
This meticulous approach ensures that each test is valuable, actionable, and aligned with your broader goals, setting you on the path to continuous optimization and growth.
Conclusion
Crafting a perfect A/B testing hypothesis is crucial for driving meaningful improvements in your e-commerce performance. By following this step-by-step guide, you ensure that your tests are well-structured, actionable, and grounded in data.
Recap:
- Identify the Problem: Start with a clear understanding of the issue you want to address.
- Gather Data: Use analytics and user feedback to inform your hypothesis.
- Define Variables: Clearly specify what you will change and measure.
- Formulate Hypothesis: Create a precise and testable hypothesis.
- Ensure Specificity and Actionability: Make sure your hypothesis is clear and feasible.
- Test for Feasibility and Prioritize: Evaluate and rank your hypotheses based on impact and resources.
- Review and Refine: Seek feedback and fine-tune your hypothesis for clarity and effectiveness.
Remember, a well-defined hypothesis not only guides your A/B tests but also maximizes the chances of obtaining actionable insights. This leads to informed decision-making and continuous optimization of your e-commerce strategies.
A/B testing is an ongoing journey. Each test provides valuable lessons that help you refine your approach and achieve better results over time. Stay curious, be diligent, and keep testing to unlock the full potential of your e-commerce site.
By implementing these steps, you’ll be well on your way to crafting hypotheses that drive real, measurable improvements. Happy testing!